Deployment configurations
This guide provides instructions for configuring your application on Galaxy. You can learn how to configure your domain name, MongoDB, and common environment variables.
Configure your domain name
The first thing you should do is verify that the deployment was successful. Check to see if the application is accessible by navigating to its URL. Then check the application logs in Galaxy at galaxy.meteor.com/app/<app_name>/logs to see if there are any errors that are affecting the deployment.
Once your application is successfully deployed, head on over to your Galaxy dashboard to configure your application by adding a custom domain name and enabling SSL encryption.
Add a domain in your application’s settings and point your DNS to:
galaxy-ingress.meteor.comfor applications in the US East region.eu-west-1.galaxy-ingress.meteor.comfor applications in the EU West region.ap-southeast-2.galaxy-ingress.meteor.comfor applications in the Asia-Pacific region.
If you are deploying to a root domain (for example mydomain.com), then follow the advanced instructions here.
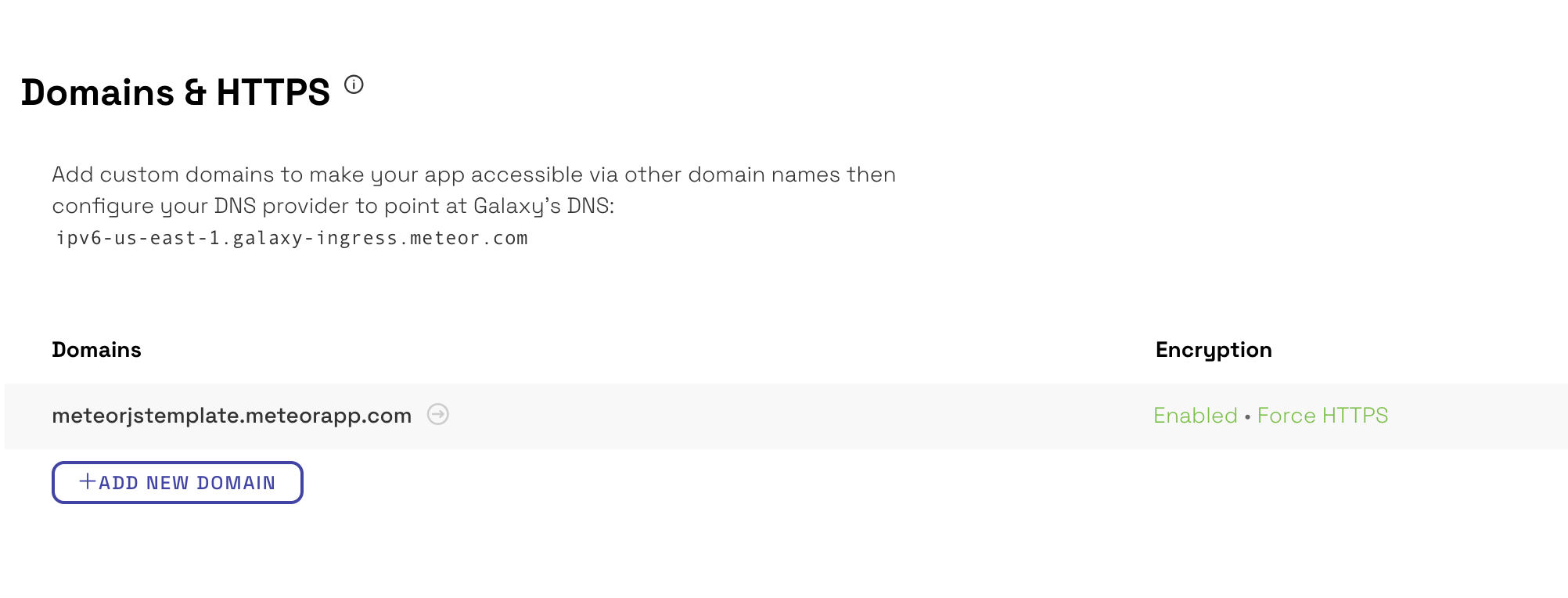
Enable encryption to secure sensitive data by generating a free Let’s Encrypt certificate by clicking on Generate Certificate or uploading your own custom certificate.

Configure your MongoDB
If your Meteor application has a package that requires Mongo, then you’ll need a Mongo database configured for your application. Most users will want to use a hosted database provider instead of running it yourselves, such as MongoDB Atlas or ScaleGrid.
For optimum performance, we recommend that you setup a database in the same AWS region as your app deployment.
Many MongoDB providers expect you to tell them what IP addresses your app will be connecting from and forbids all connections from outside those addresses. To accomplish this on Galaxy, you’ll need to run your app in IP whitelisting mode.
Create a settings file for Galaxy
Create a Meteor settings file that will define the set of configurations needed for your application to deploy and run on Galaxy. At a minimum, the settings file needs to contain the connection URL to the MongoDB database.
In your application directory, create a file named settings.json. Put the Mongo URI in the file, using this format:
{
"galaxy.meteor.com": {
"env": {
"MONGO_URL": "mongodb://<dbuser>:<dbpassword>@<dbserver>:<dbport>/<dbname>"
}
}
}
You can contact support to obscure your settings.json file. Once this is done, all app settings will be hidden across your account. A user with access to any of your app’s dashboards will not be able to view the information in your settings.json file from within the associated dashboard after this feature is enabled.
Environment variables
Environment variables in Galaxy are managed using your app’s settings.json file. Galaxy interprets key/value pairs found in the {"galaxy.meteor.com": {"env": { ... }} section of your settings as environment variables.
Note that your entire settings.json file has a size limit of approximately 32KB. If your settings file is larger than this, your containers will not run successfully. Unfortunately, there will be no clear error message in this case pointing at the root cause of the problem.
Common environment variables
The following environment variable are commonly set for Galaxy apps:
MONGO_URL: If you have any Meteor packages that requires a Mongo database, then this environment variable must be set. See your database provider instructions to determine the correct format and content for the URL. An example format would be"MONGO_URL": "mongodb://<db_username>:<db_password>@<db_server_host>:<db_server_port>/<db_name>"MONGO_OPLOG_URL: This is an optional environment variable if you are using MongoDB for your application. This is a performance optimization that we recommend for production applications. Read more in our detailed documentation. An example format would be"MONGO_OPLOG_URL": "mongodb://<oplog_username>:<oplog_password>@<db_server_host>:<db_server_port>/<oplog_db_name>?authSource=admin"ROOT_URL: This is an optional environment variable. If you have any Meteor packages that need to generate a URL, then those packages will useROOT_URLto identify the URL where the app is hosted. The default value for this is the primary hostname that your app is deployed to. This variable hooks up to theMeteor.absoluteUrl()API.MAIL_URL: This is required if you have theemailpackage in your application. In order to send email from the application, theMAIL_URLenvironment variable needs to be set. An example format would be"MAIL_URL": "smtp://postmaster%40your.mailserver.address.com:password@mailserver.smtp.address.com:587"GALAXY_NODE_OPTIONS: This is for any Node settings that can be controlled at the command line.USER_LOG_DESTINATION: This allows you to configure custom log storage.
If you’re using MongoDB, you’ll have to configure a database and a user account with rights to access that database with your database provider.
Learn more
- Learn how to configure your MongoDB provider for Galaxy.
- Deployment-specific configuration using Meteor.settings.
